Call for Papers
Scope
This special track is driven by the imperative to unravel the challenges and harness the opportunities that arise from the emerging computer and data communication networks, e.g., Metaverse and 6G networks. The requirement for the Metaverse, i.e., intelligently and securely connecting the real world to the virtual world, cannot be ignored for many future vertical industries. It will necessitate intelligent data management solutions and secured and trusted communication technologies, which can be provided by the advanced 6G networks. The paradigm shifts in 6G, as endorsed by ITU-R in Fig. 1, have promised Connecting the Unconnected, Sustainability, Ubiquitous Intelligence and Security/Privacy/Resilience.
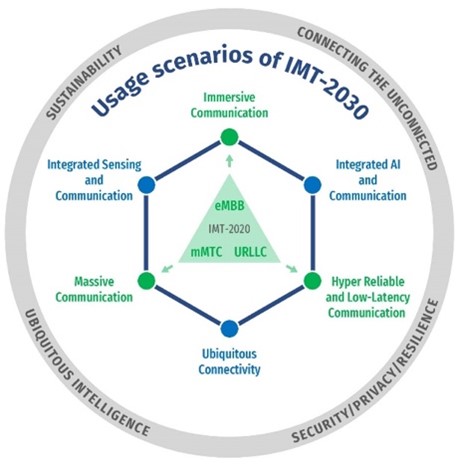
Fig. 1. The "6G Wheel" endorsed by ITU-R, illustrating the paradigm shifts that emphasize the ubiquitous intelligence and security, privacy and resilience.
Emerging use cases belonging to the 6G Metaverse scenario include dense sensor networks for vertical industries, e.g., sensate media, industry 4.0, etc. The technical difficulty here lies in developing scalable, efficient and trusted network architectures capable of accommodating the sheer volume of connected devices while mitigating interference, congestion and security issues. On the one hand, with a wide range of novel use cases including the XR and holographic communications, it would require much higher transmission bandwidth and much advanced AI-enabled network resource optimization compared to 5G. The challenge stands in developing intelligent wireless and data infrastructure capable of sustaining these bandwidth-intensive applications while ensuring a decent Quality of Experience (QoE) e.g., low latency and high reliability. On the other hand, the advanced version of mMTC, intends to support ubiquitous connectivity of a huge number of devices, and very likely in a relatively small area, with bespoke security, privacy and resilience requirements.
Witnessing the rapid development of information and communication technologies (ICT), we evince that emerging ICT technologies such as integrated sensing and communications (ISAC), AI-native networking, quantum communications, distributed ledger technology and blockchain together with intelligent data and security (IDS) solutions hold immense promise in addressing those technical challenges and difficulties associated with the Metaverse and 6G networks, which motivates this venue to pursuit the fully integrated solutions for fully unleashing the transformative potential of the Metaverse, 6G networks and future IDS. Contributions are solicited in, but not necessarily limited to, Real-time Analytics and QoE Optimization: Analysis of network performance metrics to dynamically optimize resource allocation; Machine learning models could predict user behavior and network demands based on historical throughput patterns; QoS (Quality of Service) scores could be used to proactively adjust network parameters for optimal Metaverse experience. Distributed Intelligence: Edge computing nodes could process local Metaverse data to reduce latency; Intelligent caching of frequently accessed virtual assets based on user interaction patterns; Dynamic load balancing across network cells (as shown in the cell reports) to maintain consistent performance. Security Enhancements: Blockchain-based authentication for secure virtual asset ownership; Biometric and behavioral authentication for seamless yet secure Metaverse access; Zero-trust security architecture for distributed Metaverse environments. Data Privacy: Homomorphic encryption for processing sensitive user data without exposure; Privacy-preserving machine learning techniques for user behavior analysis; Granular data access controls for different virtual spaces and assets. And also Network Security: AI-powered threat detection using network telemetry data; Quantum-safe encryption for long-term data protection; Secure network slicing for isolated Metaverse environments.
Here, one aspect worth mentioning is the clear societal and economic impacts linking with the cusp of the Metaverse and 6G networks, evidenced by national/international programs running by, e.g., UK DSIT, ESCWA, China MIIT, etc., and therefore this special track is bound to attract significant attendees and submission attention also from local authorities and public sectors.
Topics
Accepted papers will be published in the IEEE BigDataSecurity/HPSC/IDS/SmartCloud 2025 proceedings and will be submitted to the IEEE digital library (IEEE Xplore). Authors are welcome to submit original papers (not published before and/or simultaneously to another venue) with topics that include but are not limited to:
- Intelligent signal processing for 6G Metaverse with IDS
- Intelligent communication and networking for 6G Metaverse with IDS
- Integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) for 6G Metaverse with IDS
- Satellite and terrestrial network integration in 6G Metaverse with IDS
- Semantic communications for 6G Metaverse with IDS
- Next-generation massive connectivity protocols
- Next-generation network architecture
- AI-based spectrum management and allocation
- Network security and privacy in 6G
- AI-based cross-layer optimization and security
- Real-world implementations and use cases.
Planned Format
- Acceptance notification: April 9th, 2025
- Camera ready: April 15th, 2025
- Registration deadline: April 15th, 2025
- Conference date: May 9th-11th, 2025
Submission Link: https://easychair.org/account2/signin?l=3607313098226878727
Technically Sponsored by IEEE and IEEE Computer Society
Track Chairs
| Names | Affiliations |
|---|---|
| Prof. De Mi | Birmingham City University, UK |
| Prof. Zhen Gao | Beijing Institute of Technology, China |
| Prof. Derrick Wing Kwan Ng | University of New South Wales, Australia |
| Prof. Sami Muhaidat | Khalifa University, UAE |
| Dr. Xu (Tony) Xia | China Telecom Research Institute, China |
If you have any questions, please contact our Track Chair: Dr. De Mi, de.mi@bcu.ac.uk
Honorary Chairs:
- Meikang Qiu, Augusta University
- Pei Xiao, University of Surrey
- Chen Lu, Shenzhen Institute of Information Technology
- Jintao Zhang, Marinesat Network Technology Co., Ltd
- Feng Chen, Zhejiang Vie Science & Technology Co., Ltd
- Merouane Debbah, Khalifa University
- Kai-Kit Wong, University College London
- Bruno Clerckx, Imperial College London
- Zehui Xiong, Singapore University of Technology and Design
- Miaowen Wen, South China University of Technology
- Wai Ho Mow, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
- Lexi Xu, China Unicom
- Yu Su, China Mobile Chengdu Institute of Research & Development
- Wei Wang, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Technical Program Committee
- Berna Bulut Cebecioglu (Co-Chair), Birmingham City University
- Haitham Mahmoud (Co-Chair), Birmingham City University
- Li Qiao (Co-Chair), University of Surrey
- Ziwei Wan (Co-Chair), University of Surrey
- Changsheng You, Southern University of Science and Technology
- Didar Yedilkhan, Astana IT University
- Freddy Y.P. Feng, Shenzhen Institute of Information Technology
- Haoting Liu, University of Science and Technology Beijing
- Jiajie Xu, King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
- Omar Alkadri, University of Doha for Science and Technology
- Tianqi Mao, Beijing Institute of Technology
- Tianming Ma, Shanghai University of Engineering Science
- Xianghao Yu, City University of Hong Kong
- Yussuf Hassan Ahmed, Birmingham City University


